Every July, the State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI) report drops — and for anyone tracking global hunger, diet affordability, or food policy, it’s essential reading. Produced by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and its partners, SOFI offers the most authoritative annual snapshot of where we stand on food security and nutrition.
This year’s report shows cautious progress: global hunger is down slightly, but the cost of a healthy diet remains out of reach for billions. Inflation, inequality, and fragility are reshaping who eats well — and who doesn’t.
HUNGER: Some Progress, But Too Many Still Go Hungry
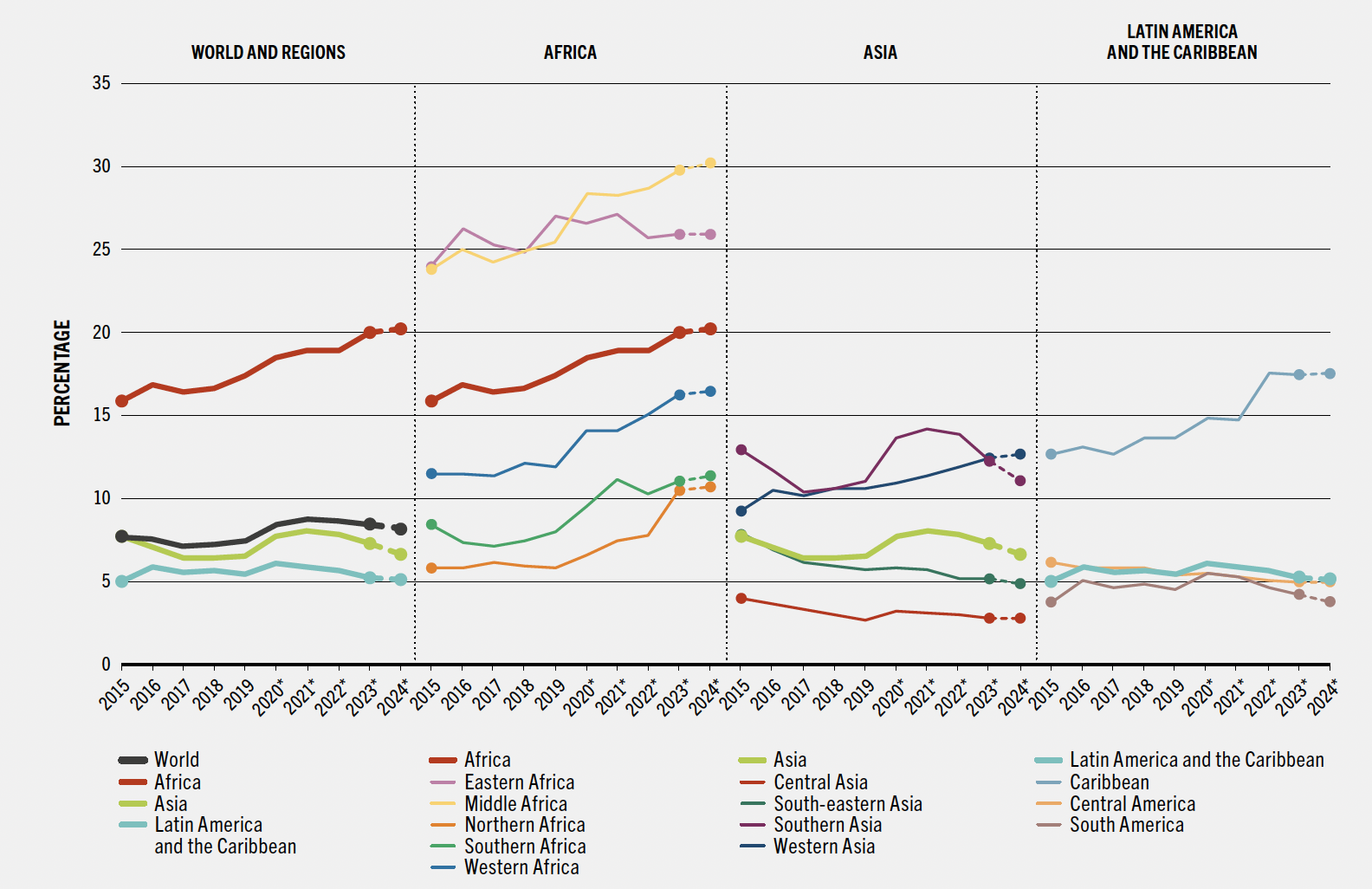
Hunger, as measured by the Prevalence of Undernourishment (PoU), dropped from 8.7% in 2022 to 8.2% in 2024 — a reduction of 15 million people since last year and 22 million since 2022. That means an estimated 673 million people still go to bed hungry. It’s progress, and progress is worth celebrating, especially after several years of worsening trends.
There have been gains in food security in Asia and Latin America, but hunger has worsened in Africa. In 2024, over 20% of Africa’s population — 307 million people — are estimated to be hungry.
Women and rural communities continue to be disproportionately affected by food insecurity.
If this trajectory continues, 511 million people are projected to be hungry by 2030 — 60% of them in Africa. Meanwhile, the global prevalence of moderate or severe food insecurity — which captures people's experiences of constrained access to adequate food — dipped slightly from 28.4% in 2023 to 28.0% in 2024, affecting 2.3 billion people.
Prevalence of undernourishment from 2015 to 2024 across world, regions and sub-regions (FAO SOFI 2025)
FOOD AFFORDABILITY: Still Out of Reach for Billions
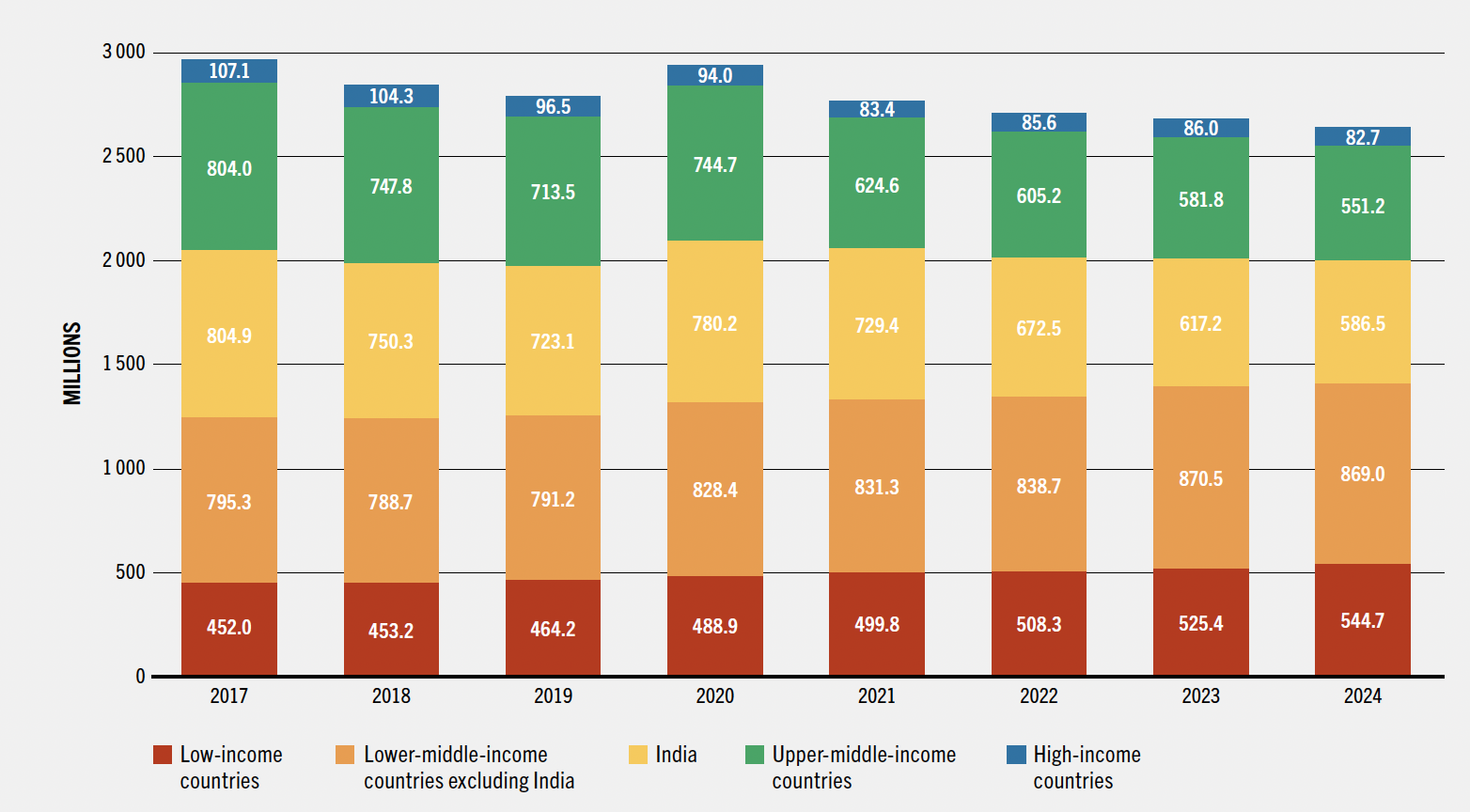
A healthy diet remains unaffordable for 2.6 billion people — though that’s down from 2.9 billion in 2020. Fruits, vegetables, and animal source foods (ASF) consistently cost the most per calorie, while ultra-processed foods are often the cheapest (a data point not in the report, but worth noting — nearly 60% of the American diet is made up of highly processed foods).
Affordability challenges are rising in many places, particularly in low-income countries. The inability to afford a healthy diet disproportionately affects the poor and is a major driver of food insecurity and malnutrition.
The millions who cannot afford a healthy diet from 2017 to 2024: low to high income countries (FAO SOFI 2025)
FOOD INFLATION: A Major Driver of Unaffordability
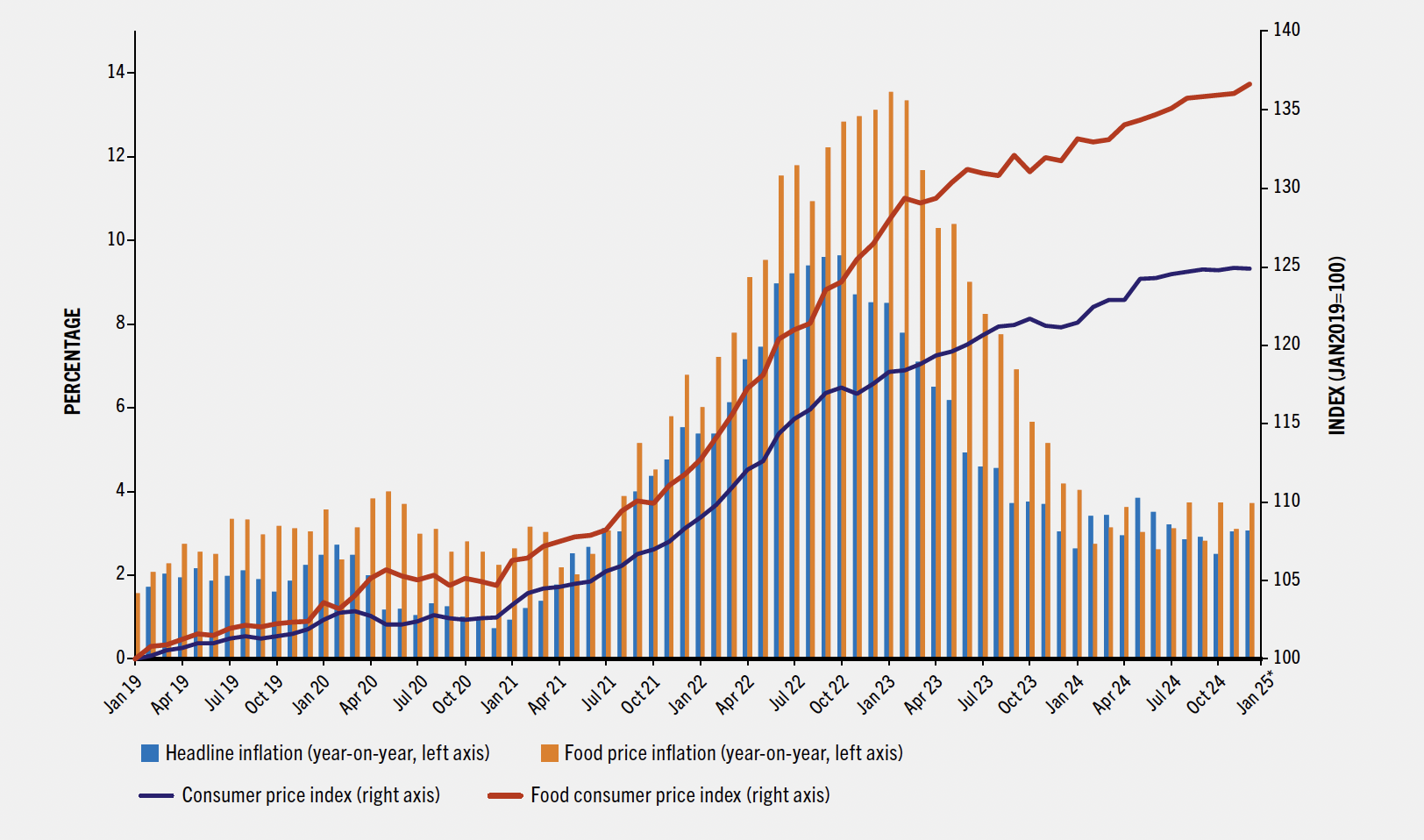
Global food prices surged in 2023 and 2024, pushing the average cost of a healthy diet to $4.46 PPP per person per day — up from $4.30 in 2023 and $4.01 in 2022. Food price inflation jumped from 2.3% in 2020 to 13.6% in 2023, far outpacing headline inflation (8.5%).
Unlike commodity price indices that track items like soybeans or sugar, this metric reflects the cost of what people actually eat. And those costs are going up — fast.
WHY FOOD INFLATION? It's Not Just the War and COVID
The COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine triggered dramatic spikes in global food commodity prices in 2021 and 2022, amplified further by rising energy costs. In the U.S. and the euro area, these shocks explained 47% and 35% of peak food inflation, respectively. The rest came from other factors: higher labor costs, exchange rate shifts, increased profit margins along supply chains, and extreme weather events that hit major breadbasket regions.
Meanwhile, governments injected $17 trillion in fiscal support during the pandemic, while consumption rebounded sharply in 2022. The U.S. dollar appreciated by over 20% compared to low- and middle-income country currencies by 2022, and the U.S. Federal Reserve expanded the monetary supply by $2.2 trillion over four years. The result? Domestic food inflation has remained stubbornly high.
WHO IS MOST IMPACTED? The Poor, Women, and Rural Communities
Food inflation hits low-income households the hardest, since they spend a larger share of their income on food. In many countries, wages haven’t kept pace. Purchasing power for food continues to vary widely, especially in fragile and conflict-affected settings like Syria.
A 10% increase in food prices is associated with a 3.5% rise in food insecurity, a 5.5% rise in child wasting, and a 3.5% rise in stunting.
Food price inflation as compared to headline inflation and food the consumer price index (FAO SOFI 2025)
NUTRITION: Mixed News
There’s been slow but real progress on reducing childhood stunting — down from 26.4% in 2012 to 23.2% in 2024. Given how hard it is to shift chronic undernutrition, this is meaningful progress but still way too slow. Wasting is flatlined and anemia among women has worsened. But obesity is rising across all age groups. And globally, we’re not on track to meet any of the major nutrition targets.
What can be done?
There’s no silver bullet — but there are well-known, proven policy actions:
Subsidize healthy foods for low-income families
Expand climate insurance and risk protection for farmers
Reduce trade restrictions that limit food exports
Scale social protection programs to shield vulnerable households
Ensure transparent monetary policy to tame inflation
Invest in agri-food R&D, transport and storage infrastructure, and real-time market information systems to build long-term resilience and reduce volatility.
I spoke to CBS Evening News last night, summarizing the latest. Check out the video below.